Polyester fibers and fabrics have been widely used in clothing, home decoration, accessories and industrial applications. In the clothing neighborhood, the polyester layer can be used for shirts, dresses, jackets, sportswear, work clothes, underwear, swimsuits, hats, scarves, gloves and headbands. Home and Lifestyle,Polyester items found around the home including bedding (sheets, pillowcases, blankets and duvet covers), curtains, upholstery (sofa covers, cushions and mattress padding), tablecloths rugs microfiber towels as well as fiberfill used as stuffing in pillows toys duvets as well as mouse pads and soft mats made with polyester fiberfill stuffing material. In industry and technology, polyester can be used in automotive carpets, seat covers, etc., conveyor belts, industrial ropes and reinforcement materials, as well as conveyor belts and industrial ropes and reinforcement materials. Polyester is used in special applications and handicrafts, such as dielectric films used in plastic bottles and electronic products. Also, in raincoats, reusable bags, plush toys, ornaments, polyester fiber is required.

Recycling
Polyester recycling is divided into mechanical and chemical. Mechanical recycling requires melting the liquid form of polyester material (usually in used textiles or plastic bottles) and then cooling, solidifying and processing into particles, which can then be spun into new fibers. Chemical recycling uses polyester to decompose polyester into its component monomers, such as glycolysis or hydrolysis. Chemical recycling can be complex and expensive than mechanical recycling, but performs an environmentally friendly process to effectively separate the polyester into the cotton mixture, and both fibers can be reused.


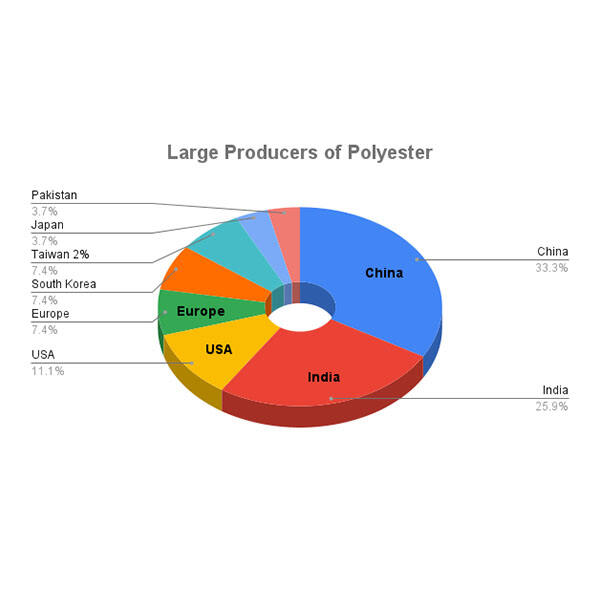
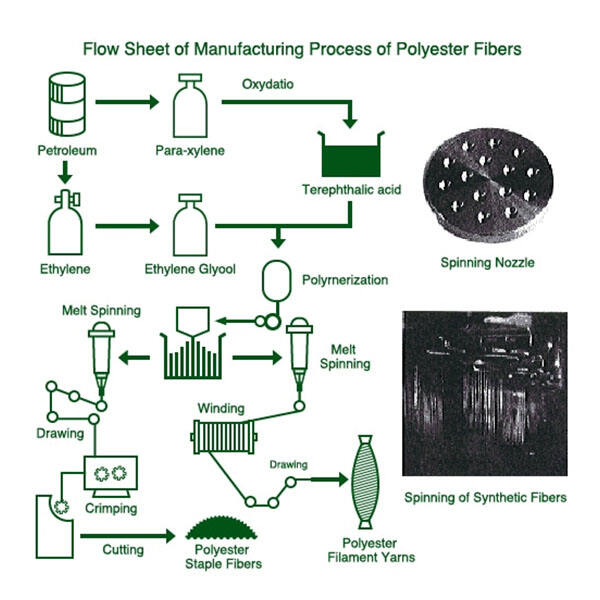


 Hot News
Hot News