יישומים של בדים אנטי-בקטריאליים
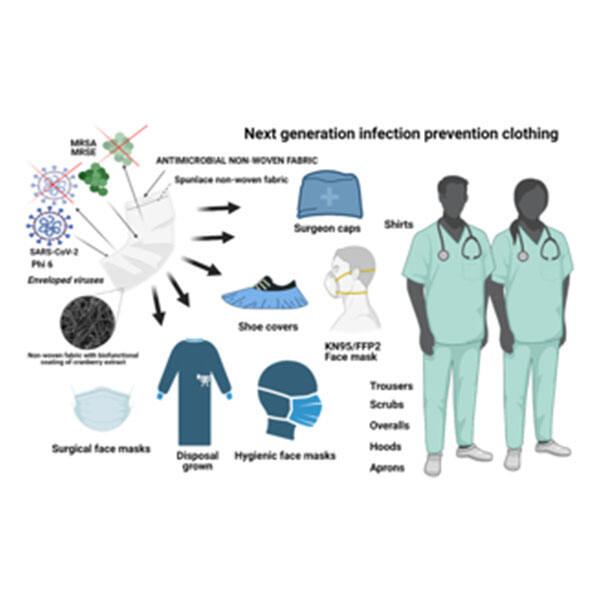
רפואי: חומרים אנטימיקרוביאליים יכולים לשמש בפריטים כמו מיטות בית חולים, מסכי חדר, מדים רפואיים וחצאיות בית חולה, guna להפחית משמעותית את סיכן הדבקה. מלונות: חומרים אנטימיקרוביאליים יכולים לשמש בפריטים כמו מיטות ומטפחות אורחים, guna ליצור סביבה נקייה. בגדים: תכונות אנטימיקרוביאליות יכולות להתווסף לבגדים, במיוחד לבגדים ספורטיביים, guna לשלוט בריח הזיעה ולשמור על טריות הבגדים במהלך פעילות גופנית. טקסטיל ל вне: חומרים אנטימיקרוביאליים יכולים להתווסף לצלעות, אוהלים וריהוט חוץ guna להאריך את תקופת השימוש ולצמצם את כמות החיידקים שנוגעים בגוף האדם. חדרי ניקיון ומעבדות: חומרים אנטימיקרוביאליים יכולים לשמש במקומות עם דרישות ניקיון קפדניות guna למנוע זיהום מיקרוביאלי. אריזה ואביזרי טקסטיל: תיקים, מטפחות או חליפות אמבטיה אנטימיקרוביאליים יכולים לשמש guna למנוע הצטברות חיידקים נוספות ולשמור על רמות ההיגיינה.
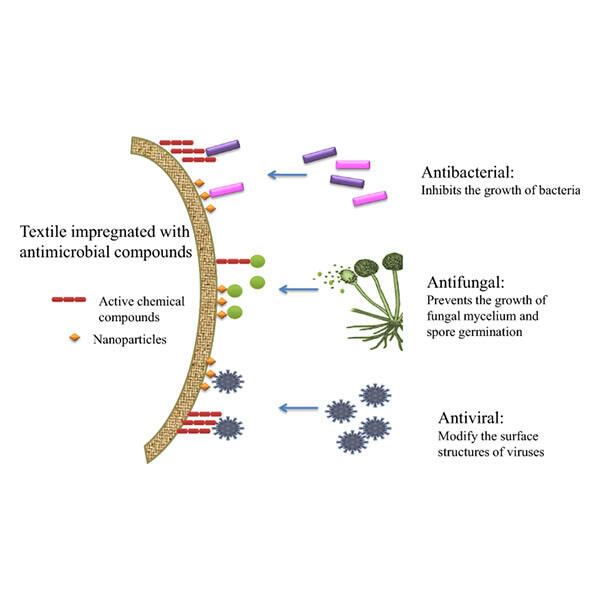
המונח "בד 100% אנטיבקטרי" אינו בהכרח מתייחס לבדים חסרי בקטריות; אלא, ניתן לעצב בדים מהנדסים בעלי יעילות אנטיבקטרית גבוהה במיוחד - לעיתים אפילו חיסול של יותר מ-99.9999% מהבקטריות תוך 24 שעות! בדים ננוקומפוזיטיים של זין, שמיוצרים באמצעות ננו-חלקיקי אבץ שצומחים בתוך הבד, הדגימו יעילות אנטיבקטרית של 99.99% עד 99.9999% תוך 24 שעות, וההגנה הזו נותרת עקבית גם לאחר 50 או 100 מחזורים של כביסה, מה שמראה על קיימות ארוכת טווח של הפעולה האנטיבקטרית, מבלי לאבד יעילות עם הזמן. בדים אנטיבקטריים מתקדמים אחרים משתמשים בטכנולוגיית יוני כסף (ולא ננו-חלקיקים) להגנה אנטימיקרוביאלית מתמשכת נגד גדילה של בקטריות, פטריות ואלגות על פני שטח הבד. זה שומר על הבדים נקיים, טריים, היגייניים ובטוחים נגד אלרגיות עור לתקופות ממושכות. טכניקות מתקדמות כמו Swiss HeiQ Viroblock משולבות בבדים מתקדמים הניתנים לשימוש חוזר מספר רב של פעמים לאחר הכביסה, מבלי לאבד את היעילות. סיום אנטימיקרוביאלי מכיל רכיבים פעילים שמקורם ב-100% צמחי, ומעניקים לבדים פעילות אנטיבקטרית ואנטימיקרוביאלית, תוך שמירה על הסביבה ועל הקיימות, ומאריכים את התחושה של טריות ומקטינים את תדירות הכביסה.
הביקוש הגובר לרקמה אנטי-בakterיאלית
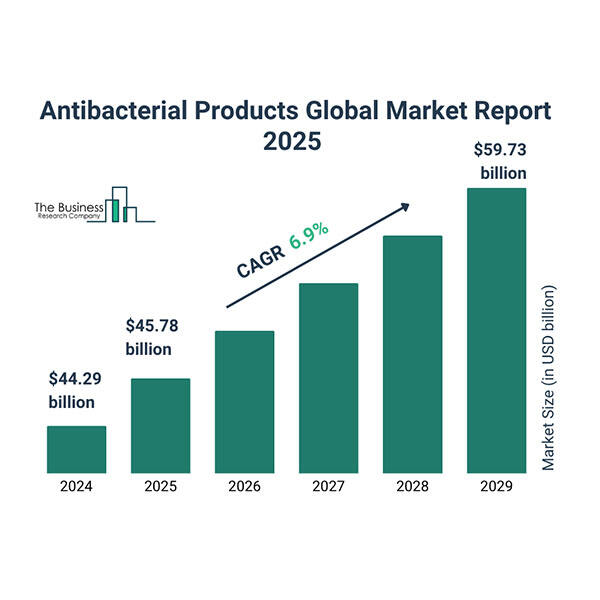
בשל הדרישות הגוברות בתחום הבריאות, סטנדרטים מוגזמים של היגיינה והצורך הגובר במניעת זיהומים במגוון תחומים, הביקוש למצעים אנטימיקרוביאליים נמצא בעלייה מתמדת. שוק המצעים האנטימיקרוביאליים העולמי מוערך בכ-2.5 מיליארד דולר לשנת 2025, עם קצב צמיחה שנתי מצטבר של 7-10% עד שנת 2033. צמיחה מהירה זו נובעת מגורמים כגון העלייה המטרידה בתחלואה של זיהומים הקשורים לבריאות (HAIs), עם עירור התודעה הציבורית בנוגע להיגיינה, וההרחבת השימוש במצעים אנטימיקרוביאליים במצעים רפואיים, לבוש (ביגוד ספורט/תחתונים), וריהוט ביתי (כגון סדינים/ריפוד). קפיצות טכנולוגיות כמו ננוטכנולוגיה (למשל ננו-חלקיקים של כסף ואוקסיד צינק) וagents אנטימיקרוביאליים ממקורות ביולוגיים תורמות להרחיב את השוק על ידי ייצור מצעים אנטימיקרוביאליים יעילים, עמידים וברורים יותר. דרישות רגולטוריות תורמות אף הן לקליטת המוצרים הללו. אזוריamente, צפון אמריקה ואירופה מובילים כיום את התפתחות תשתיות הבריאות והמודעות להיגיינה; עם זאת, השוק באסיה-แปסיפיק צפוי לגדול בקצב מהיר יותר בשל הכנסות פנויה גוברות ותשתיות רפואיות משופרות. בנוסף ליתרונות, למצעים אנטימיקרוביאליים יש גם אתגרים, בהם עלותם הגבוהה בהשוואה למצעים מסורתיים, וכן דאגות בנוגע לבטחה ארוכת טווח ותגובה נגד סוכנים מסוימים; עם זאת, מחקר ופיתוח מתמשך מכוון למציאת פתרונות ברורים ויעילים יותר מבחינה כלכלית.



 חדשות חמות
חדשות חמות